ENISA issues new guidelines to support Europe’s telecom security authorities in implementing the security requirements of the European Electronic Communications Code (EECC) and the EU 5G toolbox. The guidelines and associated 5G supplement underline the importance of a common approach to telecom security for the Digital Single Market.
Today, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) published guidelines to help ensure a common approach to securing electronic communication networks and services. The publication is an update of the 2014 ENISA Technical Guideline on Security Measures under Article 13a of the EU Telecoms Framework Directive. It provides non-binding technical guidance to telecom security authorities about the security supervision required by Articles 40 and 41 of the EECC. Article 40 of the EECC contains detailed security requirements for electronic communication providers, and Article 41 empowers competent authorities with respect to the implementation and enforcement of these requirements.
EU Agency for Cybersecurity Executive Director Juhan Lepassaar said: “With the transposition of the European Electronic Communications Code approaching, the EU Agency for Cybersecurity has published new guidelines for national telecom security authorities, which aim to achieve a common high level of communications security for telecom providers and network operators in the EU.”
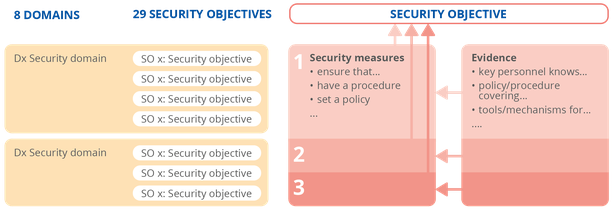
More specifically, the Guideline on Security Measures Under the EECC report contains 29 high-level security objectives listed under eight security domains (governance and risk management; human resources security; security of systems and facilities; operations management; incident management; business continuity management; monitoring, auditing and testing; threat awareness). The report also provides detailed security measures organised into three levels of increasing sophistication (basic; industry standard; state-of-the-art). Each security measure includes examples of evidence to help assess if the measures are in place.
Figure: Overall structure of the security objectives and security measures
The 5G Supplement provides national authorities with a guide to ensure the security of their 5G networks and services. The publication offers an additional step to the guideline by providing authorities with 70 proposed checks for 5G when implementing a measure or when checking the guideline’s evidence. The supplement focuses on the cybersecurity of 5G networks at the policy level stemming from the EU 5G toolbox, and includes additional information and references at the technical level for new technologies, such as virtualisation, slicing and edge computing.
The guideline and the 5G supplement were drafted in close collaboration with the ECASEC expert group of national telecom security authorities and in line with the work stream on 5G cybersecurity under the NIS Cooperation Group.
Background
The European Electronic Communication Code (EECC) replaces the existing EU Telecoms Framework Directive and brings significant changes in the security supervision of electronic communication services. The EECC requires EU Member States to implement the new rules by 21 December 2020. Established in 2010, the ECASEC Expert Group (formerly the Article 13a Expert Group) consists of more than 50 experts from national telecom security authorities from 31 EU, EFTA and EU candidate countries, who supervise the security of telecom networks and services. The expert group produces technical guidelines for European authorities on the implementation of EU telecom security rules and publishes a summary report about major telecom security incidents yearly.
Contacts
For contacting the authors please use [email protected]
For questions related to the press and interviews, please contact press (at) enisa.europa.eu

